An overlapped I/O buffer is designed to maximize the memory usage on accelerators.
This is particularly useful when there is limited accelerator memory and input
and output data. For each task instance, the ALF runtime provides an optional
overlapped I/O buffer. This buffer is accessible from the user-defined computational
kernel as well as the input_dtl_prepare and output_dtl_prepare functions.
For each overlapped I/O buffer, you can dynamically define three types of
buffer area for each work block:
- ALF_BUF_OVL_IN: Data in the host memory is copied to this section of the overlapped I/O buffer before the computational kernel is called
- ALF_BUF_OVL_OUT: Data in this buffer area of the overlapped I/O buffer is written back to the host memory after the computational kernel is called
- ALF_BUF_OVL_INOUT: Data in the host memory is copied to this buffer area before the computational kernel is called and is written back to the same host memory location after the computational kernel is called
For examples of how to use the overlapped I/O buffer, see Overlapped I/O buffer example.
Points to consider when using the overlapped I/O buffer
When
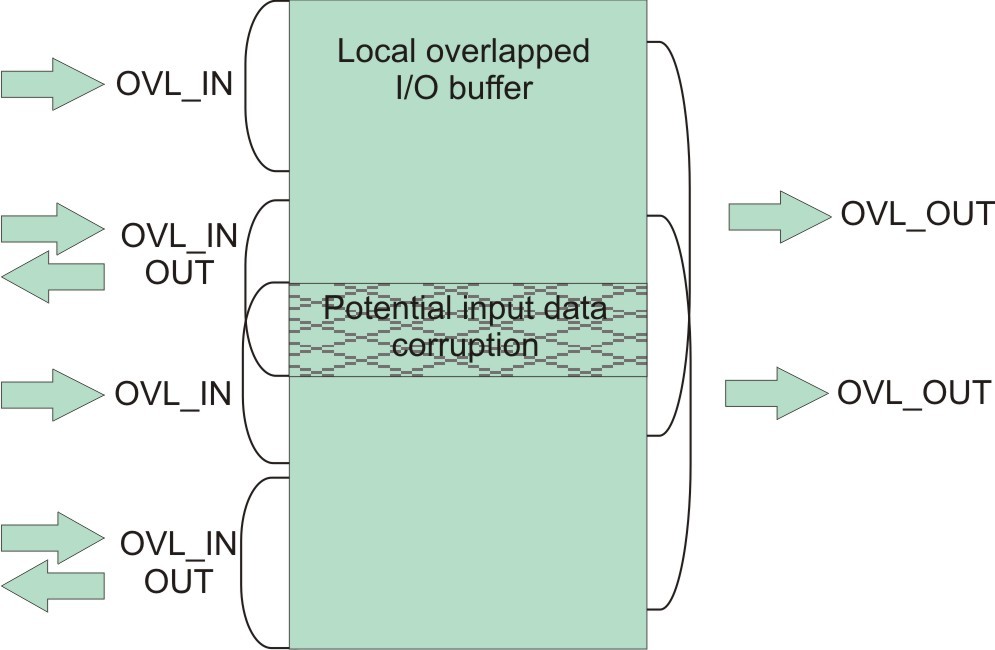
you use overlapped I/O buffer, you need to make sure that the input data area
defined by ALF_BUF_OVL_IN and ALF_BUF_OVL_INOUT do
not overlap each other. The ALF runtime does not guarantee the order in which
the input data is pulled into accelerator memory, so the input data can become
corrupted if these two areas are overlapped. Figure 1 shows
a corrupted overlapped I/O buffer.
If you choose to partition data on the accelerator, you need to generate the data transfer lists for the input buffer, the overlapped input buffer, and the overlapped I/O buffer in the user-provided alf_accel_input_dtl_prepare function and generate the data transfer lists for both the output buffer and the overlapped output buffer in the user-provided alf_accel_output_dtl_prepare function.